| PRKD2 |
|---|
 |
| Available structures |
|---|
| PDB | Ortholog search: PDBe RCSB |
|---|
| List of PDB id codes |
|---|
2COA, 3BGM, 4NNX, 4NNY |
|
|
| Identifiers |
|---|
| Aliases | PRKD2, PKD2, nPKC-D2, HSPC187, protein kinase D2 |
|---|
| External IDs | OMIM: 607074 MGI: 2141917 HomoloGene: 9516 GeneCards: PRKD2 |
|---|
| Gene location (Human) |
|---|
 | | Chr. | Chromosome 19 (human)[1] |
|---|
| | Band | 19q13.32 | Start | 46,674,275 bp[1] |
|---|
| End | 46,717,127 bp[1] |
|---|
|
| Gene location (Mouse) |
|---|
 | | Chr. | Chromosome 7 (mouse)[2] |
|---|
| | Band | 7|7 A2 | Start | 16,576,827 bp[2] |
|---|
| End | 16,604,389 bp[2] |
|---|
|
| RNA expression pattern |
|---|
| Bgee | | Human | Mouse (ortholog) |
|---|
| Top expressed in | - vena cava
- superficial temporal artery
- spleen
- body of tongue
- pylorus
- lactiferous duct
- cardia
- skin of abdomen
- pons
- blood
|
| | Top expressed in | - thymus
- spleen
- blood
- right lung
- right lung lobe
- left lung
- external carotid artery
- endocardial cushion
- lip
- internal carotid artery
|
| | More reference expression data |
|
|---|
| BioGPS | 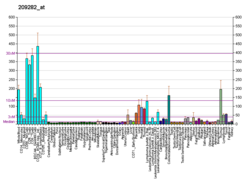
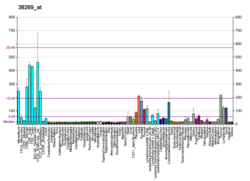 | | More reference expression data |
|
|---|
|
| Gene ontology |
|---|
| Molecular function | - transferase activity
- protein kinase activity
- nucleotide binding
- protein kinase C activity
- metal ion binding
- kinase activity
- protein binding
- ATP binding
- protein serine/threonine kinase activity
- protein kinase C binding
| | Cellular component | - cytoplasm
- Golgi apparatus
- membrane
- nucleoplasm
- nucleus
- cytosol
- plasma membrane
- intracellular anatomical structure
| | Biological process | - positive regulation of vascular endothelial growth factor receptor signaling pathway
- intracellular signal transduction
- positive regulation of endothelial cell proliferation
- adaptive immune response
- phosphorylation
- immune system process
- endothelial tube morphogenesis
- positive regulation of fibroblast growth factor receptor signaling pathway
- positive regulation of T cell receptor signaling pathway
- positive regulation of endothelial cell chemotaxis
- positive regulation of DNA-binding transcription factor activity
- cell death
- protein kinase D signaling
- positive regulation of intracellular signal transduction
- positive regulation of peptidyl-serine phosphorylation
- positive regulation of angiogenesis
- positive regulation of endothelial cell migration
- protein phosphorylation
- positive regulation of histone deacetylase activity
- positive regulation of CREB transcription factor activity
- vascular endothelial growth factor receptor signaling pathway
- cell adhesion
- positive regulation of NF-kappaB transcription factor activity
- positive regulation of interleukin-2 production
- angiogenesis
- positive regulation of interleukin-8 production
- positive regulation of blood vessel endothelial cell migration
- positive regulation of DNA biosynthetic process
- positive regulation of ERK1 and ERK2 cascade
- positive regulation of endothelial cell chemotaxis by VEGF-activated vascular endothelial growth factor receptor signaling pathway
- protein autophosphorylation
- cellular response to vascular endothelial growth factor stimulus
- T cell receptor signaling pathway
- positive regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II
- positive regulation of cell adhesion
- sphingolipid biosynthetic process
- peptidyl-serine phosphorylation
- peptidyl-threonine phosphorylation
| | Sources:Amigo / QuickGO |
|
| Orthologs |
|---|
| Species | Human | Mouse |
|---|
| Entrez | | |
|---|
| Ensembl | | |
|---|
| UniProt | | |
|---|
| RefSeq (mRNA) | |
|---|
NM_001079880
NM_001079881
NM_001079882
NM_016457 |
| |
|---|
| RefSeq (protein) | |
|---|
NP_001073349
NP_001073350
NP_001073351
NP_057541 |
| |
|---|
| Location (UCSC) | Chr 19: 46.67 – 46.72 Mb | Chr 7: 16.58 – 16.6 Mb |
|---|
| PubMed search | [3] | [4] |
|---|
|
| Wikidata |
| View/Edit Human | View/Edit Mouse |
|

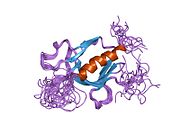 2coa: Solution structure of the PH domain of protein kinase C, D2 type from human
2coa: Solution structure of the PH domain of protein kinase C, D2 type from human





















