MARK4
| MARK4 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Identifiers | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Aliases | MARK4, MARK4L, MARK4S, MARKL1, MARKL1L, PAR-1D, microtubule affinity regulating kinase 4 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| External IDs | OMIM: 606495 MGI: 1920955 HomoloGene: 57146 GeneCards: MARK4 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Wikidata | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
MAP/microtubule affinity-regulating kinase 4 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the MARK4 gene.[5][6][7] MARK4 belongs to the family of serine/threonine kinases that phosphorylate microtubule-associated proteins (MAP) causing their detachment from microtubules.[8] Detachment thereby increases microtubule dynamics and facilitates a number of cell activities including cell division, cell cycle control, cell polarity determination, and cell shape alterations.[9]
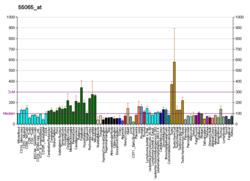
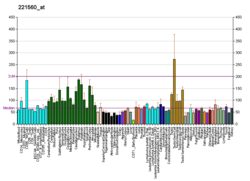
There are four members of the MARK protein family, MARK1-4, which are highly conserved. MARK4 kinase has been shown to be involved in microtubule organization in neuronal cells. Levels of MARK4 are elevated in Alzheimer's disease and may contribute to the pathological phosphorylation of tau protein in this disease.
Interactions
MARK4 has been shown to interact with USP9X[10] and Ubiquitin C.[10]
References
- ^ a b c GRCh38: Ensembl release 89: ENSG00000007047 – Ensembl, May 2017
- ^ a b c GRCm38: Ensembl release 89: ENSMUSG00000030397 – Ensembl, May 2017
- ^ "Human PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- ^ "Mouse PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- ^ Kato T, Satoh S, Okabe H, Kitahara O, Ono K, Kihara C, Tanaka T, Tsunoda T, Yamaoka Y, Nakamura Y, Furukawa Y (Apr 2001). "Isolation of a novel human gene, MARKL1, homologous to MARK3 and its involvement in hepatocellular carcinogenesis". Neoplasia. 3 (1): 4–9. doi:10.1038/sj.neo.7900132. PMC 1505019. PMID 11326310.
- ^ Drewes G, Ebneth A, Preuss U, Mandelkow EM, Mandelkow E (April 1997). "MARK, a novel family of protein kinases that phosphorylate microtubule-associated proteins and trigger microtubule disruption". Cell. 89 (2): 297–308. doi:10.1016/S0092-8674(00)80208-1. PMID 9108484.
- ^ "Entrez Gene: MARK4 MAP/microtubule affinity-regulating kinase 4".
- ^ Drewes G, Ebneth A, Preuss U, Mandelkow EM, Mandelkow E (April 1997). "MARK, a novel family of protein kinases that phosphorylate microtubule-associated proteins and trigger microtubule disruption". Cell. 89 (2): 297–308. doi:10.1016/s0092-8674(00)80208-1. PMID 9108484.
- ^ Naz F, Anjum F, Islam A, Ahmad F, Hassan MI (November 2013). "Microtubule affinity-regulating kinase 4: structure, function, and regulation". Cell Biochemistry and Biophysics. 67 (2): 485–99. doi:10.1007/s12013-013-9550-7. PMID 23471664. S2CID 13507976.
- ^ a b Al-Hakim AK, Zagorska A, Chapman L, Deak M, Peggie M, Alessi DR (April 2008). "Control of AMPK-related kinases by USP9X and atypical Lys(29)/Lys(33)-linked polyubiquitin chains" (PDF). The Biochemical Journal. 411 (2): 249–60. doi:10.1042/BJ20080067. PMID 18254724. S2CID 13038944.
Further reading
- Nagase T, Nakayama M, Nakajima D, Kikuno R, Ohara O (April 2001). "Prediction of the coding sequences of unidentified human genes. XX. The complete sequences of 100 new cDNA clones from brain which code for large proteins in vitro". DNA Research. 8 (2): 85–95. doi:10.1093/dnares/8.2.85. PMID 11347906.
- Beghini A, Magnani I, Roversi G, Piepoli T, Di Terlizzi S, Moroni RF, Pollo B, Fuhrman Conti AM, Cowell JK, Finocchiaro G, Larizza L (May 2003). "The neural progenitor-restricted isoform of the MARK4 gene in 19q13.2 is upregulated in human gliomas and overexpressed in a subset of glioblastoma cell lines". Oncogene. 22 (17): 2581–91. doi:10.1038/sj.onc.1206336. PMID 12735302.
- Trinczek B, Brajenovic M, Ebneth A, Drewes G (February 2004). "MARK4 is a novel microtubule-associated proteins/microtubule affinity-regulating kinase that binds to the cellular microtubule network and to centrosomes". The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 279 (7): 5915–23. doi:10.1074/jbc.M304528200. PMID 14594945.
- Brajenovic M, Joberty G, Küster B, Bouwmeester T, Drewes G (March 2004). "Comprehensive proteomic analysis of human Par protein complexes reveals an interconnected protein network". The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 279 (13): 12804–11. doi:10.1074/jbc.M312171200. PMID 14676191.
- Schneider A, Laage R, von Ahsen O, Fischer A, Rossner M, Scheek S, Grünewald S, Kuner R, Weber D, Krüger C, Klaussner B, Götz B, Hiemisch H, Newrzella D, Martin-Villalba A, Bach A, Schwaninger M (March 2004). "Identification of regulated genes during permanent focal cerebral ischaemia: characterization of the protein kinase 9b5/MARKL1/MARK4". Journal of Neurochemistry. 88 (5): 1114–26. doi:10.1046/j.1471-4159.2003.02228.x. PMID 15009667. S2CID 44856849.
- Rual JF, Venkatesan K, Hao T, Hirozane-Kishikawa T, Dricot A, Li N, Berriz GF, Gibbons FD, Dreze M, Ayivi-Guedehoussou N, Klitgord N, Simon C, Boxem M, Milstein S, Rosenberg J, Goldberg DS, Zhang LV, Wong SL, Franklin G, Li S, Albala JS, Lim J, Fraughton C, Llamosas E, Cevik S, Bex C, Lamesch P, Sikorski RS, Vandenhaute J, Zoghbi HY, Smolyar A, Bosak S, Sequerra R, Doucette-Stamm L, Cusick ME, Hill DE, Roth FP, Vidal M (October 2005). "Towards a proteome-scale map of the human protein-protein interaction network". Nature. 437 (7062): 1173–8. Bibcode:2005Natur.437.1173R. doi:10.1038/nature04209. PMID 16189514. S2CID 4427026.
- Wissing J, Jänsch L, Nimtz M, Dieterich G, Hornberger R, Kéri G, Wehland J, Daub H (March 2007). "Proteomics analysis of protein kinases by target class-selective prefractionation and tandem mass spectrometry". Molecular & Cellular Proteomics. 6 (3): 537–47. doi:10.1074/mcp.T600062-MCP200. hdl:10033/19756. PMID 17192257.
- v
- t
- e
Serine/threonine-specific protein kinases (EC 2.7.11.21-EC 2.7.11.30) | |||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |||||||||||||||||||||
Dual-specificity kinases (EC 2.7.12) | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| |||
 | This article on a gene on human chromosome 19 is a stub. You can help Wikipedia by expanding it. |
- v
- t
- e