| P63 |
|---|
 |
| 已知的結構 |
|---|
| PDB | 直系同源搜索: PDBe RCSB |
|---|
| PDBID列表 |
|---|
4A9Z、1RG6、2RMN、2Y9T、2Y9U、3QYM、3QYN、3US0、3US1、3US2、3ZY0、3ZY1 |
|
|
| 識別號 |
|---|
| 别名 | TP63;, AIS, B(p51A), B(p51B), EEC3, KET, LMS, NBP, OFC8, RHS, SHFM4, TP53CP, TP53L, TP73L, p40, p51, p53CP, p63, p73H, p73L, tumor protein p63 |
|---|
| 外部ID | OMIM:603273 MGI:1330810 HomoloGene:31189 GeneCards:TP63 |
|---|
|
| 相關疾病 |
|---|
| 肺腺癌、lymphoblastic leukemia、肺癌、ADULT綜合徵、附肢-乳腺綜合徵、AEC綜合徵、split hand-foot malformation 2[1] |
|
|
| RNA表达模式 |
|---|

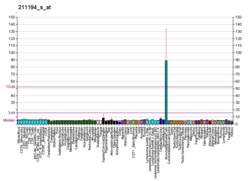
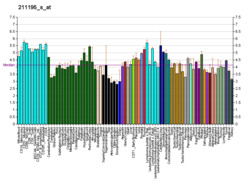 |
| 查阅更多表达数据 |
| 基因本體 |
|---|
| 分子功能 | • DNA-binding transcription activator activity, RNA polymerase II-specific
• 金屬離子結合
• damaged DNA binding
• 血浆蛋白结合
• WW domain binding
• double-stranded DNA binding
• DNA结合
• sequence-specific DNA binding
• 相同蛋白质结合
• chromatin binding
• p53 binding
• DNA结合转录因子活性
• MDM2/MDM4 family protein binding
• DNA-binding transcription factor activity, RNA polymerase II-specific
• protein domain specific binding
|
|---|
| 細胞組分 | • 細胞質
• neuron projection
• 细胞核
• 粗面内质网
• 轉錄調節複合物
• 核质
• 树突
• 線粒體
• 高尔基体
• 细胞质基质
• 大分子复合体
|
|---|
| 生物學過程 | • pattern specification process
• 骨骼系统的发生
• epithelial cell development
• negative regulation of keratinocyte differentiation
• epidermal cell division
• anatomical structure formation involved in morphogenesis
• prostate gland development
• transcription by RNA polymerase II
• squamous basal epithelial stem cell differentiation involved in prostate gland acinus development
• ectoderm and mesoderm interaction
• cellular response to DNA damage stimulus
• female genitalia morphogenesis
• odontogenesis of dentin-containing tooth
• prostatic bud formation
• positive regulation of cell cycle G1/S phase transition
• positive regulation of mesenchymal cell proliferation
• 精子发生
• multicellular organism aging
• smooth muscle tissue development
• positive regulation of fibroblast apoptotic process
• animal organ morphogenesis
• hair follicle morphogenesis
• positive regulation of Notch signaling pathway
• 细胞凋亡
• 染色体重建
• regulation of transcription, DNA-templated
• regulation of neuron apoptotic process
• positive regulation of apoptotic signaling pathway
• regulation of cysteine-type endopeptidase activity involved in apoptotic process
• transcription, DNA-templated
• embryonic limb morphogenesis
• negative regulation of mesoderm development
• epidermis development
• post-anal tail morphogenesis
• response to gamma radiation
• protein homotetramerization
• Notch信号通路
• hair follicle development
• neuron apoptotic process
• polarized epithelial cell differentiation
• proximal/distal pattern formation
• 细胞分化
• positive regulation of keratinocyte proliferation
• skin morphogenesis
• epithelial cell differentiation
• 膀胱的发生
• cellular response to UV
• establishment of planar polarity
• negative regulation of apoptotic process
• negative regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II
• protein tetramerization
• keratinocyte proliferation
• positive regulation of osteoblast differentiation
• regulation of epidermal cell division
• negative regulation of transcription, DNA-templated
• negative regulation of cellular senescence
• intrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway in response to DNA damage by p53 class mediator
• sympathetic nervous system development
• establishment of skin barrier
• morphogenesis of a polarized epithelium
• keratinocyte differentiation
• multicellular organism development
• mitotic G1 DNA damage checkpoint signaling
• cloacal septation
• response to X-ray
• positive regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II
• DNA damage response, signal transduction by p53 class mediator resulting in transcription of p21 class mediator
• positive regulation of protein insertion into mitochondrial membrane involved in apoptotic signaling pathway
• regulation of signal transduction by p53 class mediator
• regulation of apoptotic process
• 老化
• negative regulation of intracellular estrogen receptor signaling pathway
• positive regulation of transcription, DNA-templated
• positive regulation of somatic stem cell population maintenance
• 細胞增殖
• epidermal cell differentiation
• embryonic forelimb morphogenesis
• embryonic hindlimb morphogenesis
• skin epidermis development
• cranial skeletal system development
• 发育过程
|
|---|
| Sources:Amigo / QuickGO |
|
| 直系同源 |
|---|
| 物種 | 人類 | 小鼠 |
|---|
| Entrez | | |
|---|
| Ensembl | | |
|---|
| UniProt | | |
|---|
| mRNA序列 | NM_001114978
NM_001114979
NM_001114980
NM_001114981
NM_001114982
|
|---|
NM_003722
NM_001329144
NM_001329145
NM_001329146
NM_001329148
NM_001329149
NM_001329150
NM_001329964 |
| NM_001127259
NM_001127260
NM_001127261
NM_001127262
NM_001127263
|
|---|
NM_001127264
NM_001127265
NM_011641 |
|
|---|
| 蛋白序列 | NP_001108450
NP_001108451
NP_001108452
NP_001108453
NP_001108454
|
|---|
NP_001316073
NP_001316074
NP_001316075
NP_001316077
NP_001316078
NP_001316079
NP_001316893
NP_003713 |
| NP_001120731
NP_001120732
NP_001120733
NP_001120734
NP_001120735
|
|---|
NP_001120736
NP_001120737
NP_035771 |
|
|---|
| 基因位置(UCSC) | Chr 3: 189.63 – 189.9 Mb | Chr 16: 25.5 – 25.71 Mb |
|---|
| PubMed查找 | [4] | [5] |
|---|
| 維基數據 |
|




 . PMID 21335238. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2011.01.013.
. PMID 21335238. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2011.01.013.  . PMID 19570515. doi:10.1016/j.stem.2009.04.003.
. PMID 19570515. doi:10.1016/j.stem.2009.04.003.  . PMID 21331089. doi:10.1038/nrg2933.
. PMID 21331089. doi:10.1038/nrg2933.  . PMID 12037717. doi:10.1086/341450.
. PMID 12037717. doi:10.1086/341450.  . PMID 16187309. doi:10.1002/bdrc.20047.
. PMID 16187309. doi:10.1002/bdrc.20047.  . PMID 21127502. doi:10.1038/cdd.2010.159.
. PMID 21127502. doi:10.1038/cdd.2010.159. 
















