UPGMA (unweighted pair group method with arithmetic mean )是一種相對簡單的層次聚類 方法。這個方法存在另一種變體 WPGMA。這個方法的創始人被認為是Sokal 和Michener 。 [1]
演算方法 UPGMA 演法構建出一棵有根樹(樹狀圖)表現相似矩陣或相異矩陣 中的特徵與結構。在算法裡的每一步,距離最近的兩個集群(子樹)將被組合成一個更高級別的集群。任意兩個集群 A {\displaystyle {\mathcal {A}}} B {\displaystyle {\mathcal {B}}} A {\displaystyle {\mathcal {A}}} x {\displaystyle x} B {\displaystyle {\mathcal {B}}} y {\displaystyle y} d ( x , y ) {\displaystyle d(x,y)} | A | {\displaystyle {|{\mathcal {A}}|}} | B | {\displaystyle {|{\mathcal {B}}|}}
d A , B = 1 | A | ⋅ | B | ∑ x ∈ A ∑ y ∈ B d ( x , y ) {\displaystyle d_{{\mathcal {A}},{\mathcal {B}}}={1 \over {|{\mathcal {A}}|\cdot |{\mathcal {B}}|}}\sum _{x\in {\mathcal {A}}}\sum _{y\in {\mathcal {B}}}d(x,y)} 換句話說,在每一次組合成新集群的步驟中,可以由 d A , X {\displaystyle d_{{\mathcal {A}},X}} d B , X {\displaystyle d_{{\mathcal {B}},X}} A ∪ B {\displaystyle {\mathcal {A}}\cup {\mathcal {B}}} X {\displaystyle X}
d ( A ∪ B ) , X = | A | ⋅ d A , X + | B | ⋅ d B , X | A | + | B | {\displaystyle d_{({\mathcal {A}}\cup {\mathcal {B}}),X}={\frac {|{\mathcal {A}}|\cdot d_{{\mathcal {A}},X}+|{\mathcal {B}}|\cdot d_{{\mathcal {B}},X}}{|{\mathcal {A}}|+|{\mathcal {B}}|}}}
UPGMA 演算法生成的有根樹狀圖是一個超度量 樹,該樹需要套用等速率的假設,也就是說根到每個分支尖端的距離皆相等。當尖端是同時採樣的分子數據(即DNA 、 RNA 和蛋白質 )時,超度量 假設就等同於分子鐘 假設。
示例 這個示例是基於JC69基因距離矩陣,該矩陣是根據五種細菌的5S 核糖體 RNA 序列計算出來的,五種細菌如下所列[2] [3]
枯草桿菌 Bacillus subtilis ( a {\displaystyle a}
嗜热脂肪芽孢杆菌 <i>Bacillus stearothermophilus</i>( b {\displaystyle b}
魏斯氏菌 Lactobacillus viridescens ( c {\displaystyle c}
無原枯草桿菌 Acholeplasma modicum ( d {\displaystyle d}
藤黄微球菌 <i>Micrococcus luteus</i>( e {\displaystyle e}
第一步 假設有五個物件 ( a , b , c , d , e ) {\displaystyle (a,b,c,d,e)} D 1 {\displaystyle D_{1}}
a b c d e a 0 17 21 31 23 b 17 0 30 34 21 c 21 30 0 28 39 d 31 34 28 0 43 e 23 21 39 43 0
在這裡, D 1 ( a , b ) = 17 {\displaystyle D_{1}(a,b)=17} a {\displaystyle a} b {\displaystyle b}
令 u {\displaystyle u} a {\displaystyle a} b {\displaystyle b} a {\displaystyle a} b {\displaystyle b} u {\displaystyle u} δ ( a , u ) = δ ( b , u ) = D 1 ( a , b ) / 2 {\displaystyle \delta (a,u)=\delta (b,u)=D_{1}(a,b)/2} δ ( a , u ) = δ ( b , u ) = 17 / 2 = 8.5 {\displaystyle \delta (a,u)=\delta (b,u)=17/2=8.5}
然後將 D 1 {\displaystyle D_{1}} D 2 {\displaystyle D_{2}} a {\displaystyle a} b {\displaystyle b} D 2 {\displaystyle D_{2}}
D 2 ( ( a , b ) , c ) = ( D 1 ( a , c ) × 1 + D 1 ( b , c ) × 1 ) / ( 1 + 1 ) = ( 21 + 30 ) / 2 = 25.5 {\displaystyle D_{2}((a,b),c)=(D_{1}(a,c)\times 1+D_{1}(b,c)\times 1)/(1+1)=(21+30)/2=25.5}
D 2 ( ( a , b ) , d ) = ( D 1 ( a , d ) + D 1 ( b , d ) ) / 2 = ( 31 + 34 ) / 2 = 32.5 {\displaystyle D_{2}((a,b),d)=(D_{1}(a,d)+D_{1}(b,d))/2=(31+34)/2=32.5}
D 2 ( ( a , b ) , e ) = ( D 1 ( a , e ) + D 1 ( b , e ) ) / 2 = ( 23 + 21 ) / 2 = 22 {\displaystyle D_{2}((a,b),e)=(D_{1}(a,e)+D_{1}(b,e))/2=(23+21)/2=22}
D 2 {\displaystyle D_{2}}
第二步 現在重複前面的三個步驟,並從新的相異矩陣 D 2 {\displaystyle D_{2}}
(a,b) c d e (a,b) 0 25.5 32.5 22 c 25.5 0 28 39 d 32.5 28 0 43 e 22 39 43 0
在這個矩陣中, D 2 ( ( a , b ) , e ) = 22 {\displaystyle D_{2}((a,b),e)=22} D 2 {\displaystyle D_{2}} ( a , b ) {\displaystyle (a,b)} e {\displaystyle e}
令 v {\displaystyle v} ( a , b ) {\displaystyle (a,b)} e {\displaystyle e} a , b , e {\displaystyle a,b,e} v {\displaystyle v} δ ( a , v ) = δ ( b , v ) = δ ( e , v ) = 22 / 2 = 11 {\displaystyle \delta (a,v)=\delta (b,v)=\delta (e,v)=22/2=11} u {\displaystyle u} v {\displaystyle v} δ ( u , v ) = δ ( e , v ) − δ ( a , u ) = δ ( e , v ) − δ ( b , u ) = 11 − 8.5 = 2.5 {\displaystyle \delta (u,v)=\delta (e,v)-\delta (a,u)=\delta (e,v)-\delta (b,u)=11-8.5=2.5}
然後將 D 2 {\displaystyle D_{2}} D 3 {\displaystyle D_{3}}
D 3 ( ( ( a , b ) , e ) , c ) = ( D 2 ( ( a , b ) , c ) × 2 + D 2 ( e , c ) × 1 ) / ( 2 + 1 ) = ( 25.5 × 2 + 39 × 1 ) / 3 = 30 {\displaystyle D_{3}(((a,b),e),c)=(D_{2}((a,b),c)\times 2+D_{2}(e,c)\times 1)/(2+1)=(25.5\times 2+39\times 1)/3=30}
D 3 ( ( ( a , b ) , e ) , d ) = ( D 2 ( ( a , b ) , d ) × 2 + D 2 ( e , d ) × 1 ) / ( 2 + 1 ) = ( 32.5 × 2 + 43 × 1 ) / 3 = 36 {\displaystyle D_{3}(((a,b),e),d)=(D_{2}((a,b),d)\times 2+D_{2}(e,d)\times 1)/(2+1)=(32.5\times 2+43\times 1)/3=36}
第三、四步 重複上述動作可以得到 D 3 {\displaystyle D_{3}}
((a,b),e) c d ((a,b),e) 0 30 36 c 30 0 28 d 36 28 0
D 4 {\displaystyle D_{4}}
((a,b),e) (c,d) ((a,b),e) 0 33 (c,d) 33 0
UPGMA樹狀圖 這裡顯示了完成的樹狀圖。[4] a {\displaystyle a} e {\displaystyle e} r {\displaystyle r}
δ ( a , r ) = δ ( b , r ) = δ ( e , r ) = δ ( c , r ) = δ ( d , r ) = 16.5 {\displaystyle \delta (a,r)=\delta (b,r)=\delta (e,r)=\delta (c,r)=\delta (d,r)=16.5}
這個樹狀圖的根是它最深的節點 r {\displaystyle r}
時間複雜度 構建 UPGMA 樹的算法有 O ( n 3 ) {\displaystyle O(n^{3})} O ( n 2 log n ) {\displaystyle O(n^{2}\log n)} O ( n 2 ) {\displaystyle O(n^{2})} [5]
See also ^ Sokal, Michener. A statistical method for evaluating systematic relationships. University of Kansas Science Bulletin. 1958, 38 : 1409–1438. 温哥华格式错误 (帮助) ^ Erdmann VA, Wolters J. Collection of published 5S, 5.8S and 4.5S ribosomal RNA sequences. Nucleic Acids Research. 1986,. 14 Suppl (Suppl): r1–59. PMC 341310 PMID 2422630 . doi:10.1093/nar/14.suppl.r1 . ^ Olsen GJ. Phylogenetic analysis using ribosomal RNA. Methods in Enzymology. 1988, 164 : 793–812. PMID 3241556 . doi:10.1016/s0076-6879(88)64084-5 . ^ Swofford DL, Olsen GJ, Waddell PJ, Hillis DM. Hillis , 编. Phylogenetic inference. Sunderland, MA: Sinauer. 1996: 407–514. ISBN 9780878932825. ^ Murtagh F. Complexities of Hierarchic Clustering Algorithms: the state of the art. Computational Statistics Quarterly. 1984, 1 : 101–113. 外部連結 UPGMA聚类算法在Ruby中的实现(AI4R) (页面存档备份,存于互联网档案馆 ) 使用相似矩阵计算 UPGMA 的示例 (页面存档备份,存于互联网档案馆 ) 使用距离矩阵计算 UPGMA 的示例 (页面存档备份,存于互联网档案馆 ) 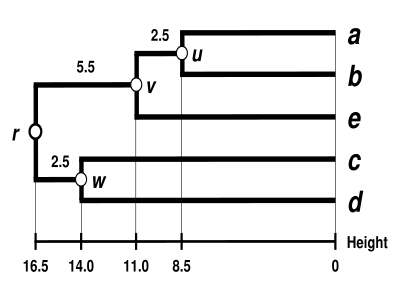
 . PMID 2422630. doi:10.1093/nar/14.suppl.r1.
. PMID 2422630. doi:10.1093/nar/14.suppl.r1. 





















































