List of extreme points of Canada
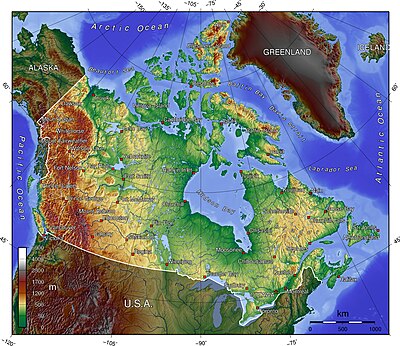
The following lists include extreme and significant points of the geography of Canada.
All Canada
- Northernmost point — Cape Columbia, Ellesmere Island, Nunavut 83°6′41″N 69°57′30″W / 83.11139°N 69.95833°W / 83.11139; -69.95833 (Cape Columbia)
- Southernmost point — South point of Middle Island, Ontario, in Lake Erie 41°40′53″N 82°40′56″W / 41.68139°N 82.68222°W / 41.68139; -82.68222 (South point of Middle Island)
- Easternmost point — Cape Spear, Newfoundland 47°31′25″N 52°37′10″W / 47.52361°N 52.61944°W / 47.52361; -52.61944 (Cape Spear)
- Westernmost point — Boundary Peak 187,[1] Yukon 60°18′23″N 141°0′7″W / 60.30639°N 141.00194°W / 60.30639; -141.00194 (Boundary Peak 187)
Non-insular (mainland) Canada
- Northernmost point — Zenith Point, Nunavut 72°0′0″N 94°38′59″W / 72.00000°N 94.64972°W / 72.00000; -94.64972 (Zenith Point)
- Southernmost point — Point Pelee, Ontario 41°54′33″N 82°30′32″W / 41.90917°N 82.50889°W / 41.90917; -82.50889 (Point Pelee)
- Easternmost point — Cape Saint Charles, Labrador 52°13′3″N 55°37′15″W / 52.21750°N 55.62083°W / 52.21750; -55.62083 (Cape Saint Charles)
- Westernmost point — Boundary Peak 187,[1] Yukon 60°18′23″N 141°0′7″W / 60.30639°N 141.00194°W / 60.30639; -141.00194 (Boundary Peak 187)
Highest points
- Mount Logan[note 1][2][3] Yukon 60°34′33″N 140°24′10″W / 60.57583°N 140.40278°W / 60.57583; -140.40278 (Mount Logan) — highest Canadian summit at 5,959 m (19,551 ft)
- Barbeau Peak,[note 2][4][5] Ellesmere Island, Nunavut 81°54′30″N 75°1′30″W / 81.90833°N 75.02500°W / 81.90833; -75.02500 (Barbeau Peak) — highest Canadian island summit and highest summit of the Canadian Arctic at 2,616 m (8,583 ft)
Lowest points
- Coastline — lowest Canadian surface point at sea level[citation needed]
- Great Slave Lake bottom, Northwest Territories 61°40′N 114°00′W / 61.667°N 114.000°W / 61.667; -114.000 (Great Slave Lake) — lowest fresh water point of North America at −458 m (−1,503 feet)
Islands
- Baffin Island, Nunavut 63°33′N 65°26′W / 63.550°N 65.433°W / 63.550; -65.433 (Baffin Island) — most extensive Canadian island at 507,451 km2 (195,928 square miles)
- Ellesmere Island, Nunavut 81°55′36″N 74°59′12″W / 81.92667°N 74.98667°W / 81.92667; -74.98667 (Ellesmere Island) — tallest Canadian island at 2,616 m (8,583 ft)
- Island of Newfoundland, Newfoundland and Labrador 49°N 56°W / 49°N 56°W / 49; -56 (Island of Newfoundland) — most extensive Canadian Atlantic island at 108,860 km2 (42,031 square miles)
- Vancouver Island, British Columbia 49°30′N 125°30′W / 49.500°N 125.500°W / 49.500; -125.500 (Vancouver Island) — most extensive Canadian Pacific island at 31,285 km2 (12,079 square miles)
- Manitoulin Island in Lake Huron, Ontario 45°46′N 82°12′W / 45.767°N 82.200°W / 45.767; -82.200 (Manitoulin Island) — most extensive lake island on Earth at 2,766 km2 (1,068 square miles)
Lakes
- Lake Superior, Ontario 47°45′N 87°30′W / 47.750°N 87.500°W / 47.750; -87.500 (Lake Superior) — most voluminous lake of Western Hemisphere at 11,600 km3 (2,800 cubic miles)
- Great Slave Lake, Northwest Territories 61°40′N 114°00′W / 61.667°N 114.000°W / 61.667; -114.000 (Great Slave Lake) — deepest lake of Western Hemisphere at 614 m (2,014 ft)
- Lake Michigan–Huron, Ontario 45°49′N 84°45′W / 45.817°N 84.750°W / 45.817; -84.750 (Lake Michigan–Huron) — by some considerations the most extensive lake of Western Hemisphere and the most extensive freshwater lake on Earth at 117,400 km2 (45,300 sq mi)[6]
- Nettilling Lake on Baffin Island, Nunavut 66°30′N 70°50′W / 66.500°N 70.833°W / 66.500; -70.833 (Nettilling Lake) — most extensive lake on an island on Earth at 5,066 km2 (1,956 square miles)
- Lake Manitou on Manitoulin Island in Lake Huron, Ontario 45°46′42″N 81°59′30″W / 45.77833°N 81.99167°W / 45.77833; -81.99167 (Lake Manitou) — most extensive lake on an island in a lake on Earth at 104 km2 (40 square miles)
- Upper Dumbell Lake on Ellesmere Island Nunavut 82°28′N 062°30′W / 82.467°N 62.500°W / 82.467; -62.500 (Upper Dumbell Lake) — most northern lake, there are more northern lakes but they are all unnamed and are only shown on detailed maps.
Rivers
- Yukon River, British Columbia, Yukon, and Alaska 62°35′55″N 164°47′40″W / 62.59861°N 164.79444°W / 62.59861; -164.79444 (Yukon River) — longest Bering Sea main stem river at 3,185 km (1,979 miles)
- Nelson River, Manitoba 57°5′5″N 92°30′8″W / 57.08472°N 92.50222°W / 57.08472; -92.50222 (Nelson River) — longest Hudson Bay main stem river at 2,575 km (1,600 miles)
- Columbia River, British Columbia 46°14′39″N 124°3′29″W / 46.24417°N 124.05806°W / 46.24417; -124.05806 (Columbia River) — longest Canadian Pacific Ocean main stem river at 2,000 km (1,243 miles)
- Mackenzie River, Northwest Territories 68°56′23″N 136°10′22″W / 68.93972°N 136.17278°W / 68.93972; -136.17278 (Mackenzie River) — longest Canadian Arctic Ocean main stem river at 1,738 km (1,080 miles)
- Saint Lawrence River, Ontario and Quebec 49°40′N 64°30′W / 49.667°N 64.500°W / 49.667; -64.500 (Saint Lawrence River) — longest Canadian Atlantic Ocean main stem river at 965 km (600 miles)
Extreme distances
- Greatest driving distance between any two points via the Canadian road network (including the Trans-Canada Highway Ferry): 9262 km from L'Anse Aux Meadows, Newfoundland and Labrador to Tuktoyatuk, Northwest Territories.
- Greatest driving distance between any two points via the Canadian road network (excluding the Trans-Canada Highway Ferry): 9156 km from Old Fort, Quebec to Tuktoyatuk, Northwest Territories.
See also
- Geography of Canada
- Extreme points of North America
- Extreme points of Canadian provinces
- Extreme communities of Canada
- Nordicity
- Remote and isolated community
Notes
- ^ The summit of Mount Logan is the highest point of the Saint Elias Mountains, the Yukon Territory, and all of Canada.
- ^ The summit of Barbeau Peak is the highest point of Ellesmere Island, the Queen Elizabeth Islands, and Nunavut.
References
- ^ a b "141st Meridian Boundary Points". International Boundary Commission. Archived from the original on 13 March 2016. Retrieved 2010-12-20.
- ^ "Mount Logan". Geographical Names of Canada. Natural Resources Canada. Archived from the original on June 16, 2013. Retrieved September 10, 2012.
- ^ "Mount Logan". Summits of the World. peakbagger.com. Retrieved September 10, 2012.
- ^ "Barbeau Peak". Geographical Names of Canada. Natural Resources Canada. Archived from the original on June 16, 2013. Retrieved September 10, 2012.
- ^ "Barbeau Peak". Summits of the World. peakbagger.com. Retrieved September 10, 2012.
- ^ Dept. of Environmental Quality, State of Michigan
External links
Canada at Wikipedia's sister projects
 Definitions from Wiktionary
Definitions from Wiktionary Media from Commons
Media from Commons News from Wikinews
News from Wikinews Quotations from Wikiquote
Quotations from Wikiquote Texts from Wikisource
Texts from Wikisource Textbooks from Wikibooks
Textbooks from Wikibooks Resources from Wikiversity
Resources from Wikiversity
- v
- t
- e
- Antigua and Barbuda
- Bahamas
- Barbados
- Belize
- Canada
- Costa Rica
- Cuba
- Dominica
- Dominican Republic
- El Salvador
- Grenada
- Guatemala
- Haiti
- Honduras
- Jamaica
- Mexico
- Nicaragua
- Panama
- Saint Kitts and Nevis
- Saint Lucia
- Saint Vincent and the Grenadines
- Trinidad and Tobago
- United States
Dependencies and
other territories
other territories
- Anguilla
- Aruba
- Bermuda
- Bonaire
- British Virgin Islands
- Cayman Islands
- Curaçao
- Greenland
- Guadeloupe
- Martinique
- Montserrat
- Puerto Rico
- Saint Barthélemy
- Saint Martin
- Saint Pierre and Miquelon
- Saba
- Sint Eustatius
- Sint Maarten
- Turks and Caicos Islands
- United States Virgin Islands





















