| CFLAR |
|---|
 |
| Available structures |
|---|
| PDB | Ortholog search: PDBe RCSB |
|---|
| List of PDB id codes |
|---|
3H11, 3H13, 2N5R |
|
|
| Identifiers |
|---|
| Aliases | CFLAR, CASH, CASP8AP1, CLARP, Casper, FLAME, FLAME-1, FLAME1, FLIP, I-FLICE, MRIT, c-FLIP, c-FLIPL, c-FLIPR, c-FLIPS, CASP8 and FADD like apoptosis regulator, cFLIP |
|---|
| External IDs | OMIM: 603599 MGI: 1336166 HomoloGene: 7652 GeneCards: CFLAR |
|---|
| Gene location (Human) |
|---|
 | | Chr. | Chromosome 2 (human)[1] |
|---|
| | Band | 2q33.1 | Start | 201,116,154 bp[1] |
|---|
| End | 201,176,687 bp[1] |
|---|
|
| Gene location (Mouse) |
|---|
 | | Chr. | Chromosome 1 (mouse)[2] |
|---|
| | Band | 1 C1.3|1 29.16 cM | Start | 58,750,667 bp[2] |
|---|
| End | 58,798,043 bp[2] |
|---|
|
| RNA expression pattern |
|---|
| Bgee | | Human | Mouse (ortholog) |
|---|
| Top expressed in | - right lung
- upper lobe of left lung
- left ventricle
- blood
- gastrocnemius muscle
- bone marrow cells
- monocyte
- renal medulla
- spleen
- lymph node
|
| | Top expressed in | - ascending aorta
- aortic valve
- proximal tubule
- right lung
- right lung lobe
- ciliary body
- thymus
- lateral recess
- retinal pigment epithelium
- left lung
|
| | More reference expression data |
|
|---|
| BioGPS | 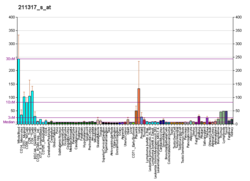
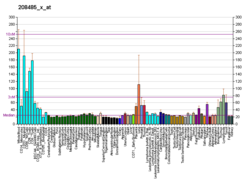
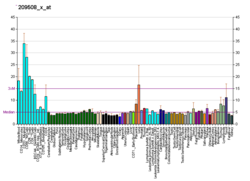 | | More reference expression data |
|
|---|
|
| Gene ontology |
|---|
| Molecular function | - cysteine-type peptidase activity
- protein binding
- cysteine-type endopeptidase activity involved in execution phase of apoptosis
- enzyme activator activity
- cysteine-type endopeptidase activity
- peptidase activator activity
- protein heterodimerization activity
- protease binding
- death receptor binding
- protein-containing complex binding
- cysteine-type endopeptidase activity involved in apoptotic process
| | Cellular component | - cytosol
- CD95 death-inducing signaling complex
- ripoptosome
- death-inducing signaling complex
- membrane raft
- cytoplasm
| | Biological process | - regulation of apoptotic process
- execution phase of apoptosis
- negative regulation of apoptotic process
- proteolysis
- positive regulation of I-kappaB kinase/NF-kappaB signaling
- regulation of necroptotic process
- regulation of extrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway via death domain receptors
- viral process
- apoptotic process
- positive regulation of catalytic activity
- response to hypoxia
- negative regulation of cardiac muscle cell apoptotic process
- positive regulation of neuron projection development
- cellular response to insulin stimulus
- response to testosterone
- positive regulation of ERK1 and ERK2 cascade
- cellular response to epidermal growth factor stimulus
- cellular response to estradiol stimulus
- cellular response to hypoxia
- cellular response to dexamethasone stimulus
- cellular response to nitric oxide
- positive regulation of glomerular mesangial cell proliferation
- positive regulation of extracellular matrix organization
- negative regulation of reactive oxygen species biosynthetic process
- negative regulation of cellular response to transforming growth factor beta stimulus
- negative regulation of hepatocyte apoptotic process
- negative regulation of epithelial cell apoptotic process
- positive regulation of hepatocyte proliferation
- negative regulation of extrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway via death domain receptors
- skeletal muscle tissue development
- positive regulation of peptidase activity
- skeletal muscle atrophy
- regulation of skeletal muscle satellite cell proliferation
- skeletal myofibril assembly
- negative regulation of cysteine-type endopeptidase activity involved in apoptotic process
- skeletal muscle tissue regeneration
- positive regulation of NF-kappaB transcription factor activity
- negative regulation of necroptotic process
- negative regulation of myoblast fusion
- negative regulation of extrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway
- response to bacterium
| | Sources:Amigo / QuickGO |
|
| Orthologs |
|---|
| Species | Human | Mouse |
|---|
| Entrez | | |
|---|
| Ensembl | | |
|---|
| UniProt | | |
|---|
| RefSeq (mRNA) | NM_001127183
NM_001127184
NM_001202515
NM_001202516
NM_001202517
|
|---|
NM_001202518
NM_001202519
NM_001308042
NM_001308043
NM_003879
NM_001351590
NM_001351591
NM_001351592
NM_001351593
NM_001351594 |
| NM_001289704
NM_001293804
NM_001293805
NM_009805
NM_207653
|
|---|
NM_001355056 |
|
|---|
| RefSeq (protein) | NP_001120655
NP_001120656
NP_001189444
NP_001189445
NP_001189446
|
|---|
NP_001189447
NP_001189448
NP_001294971
NP_001294972
NP_003870
NP_001338519
NP_001338520
NP_001338521
NP_001338522
NP_001338523 |
| NP_001276633
NP_001280733
NP_001280734
NP_033935
NP_997536
|
|---|
NP_001341985 |
|
|---|
| Location (UCSC) | Chr 2: 201.12 – 201.18 Mb | Chr 1: 58.75 – 58.8 Mb |
|---|
| PubMed search | [3] | [4] |
|---|
|
| Wikidata |
| View/Edit Human | View/Edit Mouse |
|





















